Explain Two Differences Bright Field and Phase Contrast
In this article we will learn 12 important difference between Darkfield and bright Field Microscope. Phase contrast can give you hidden details and give you a sense of the density of the specimen which can be extremely helpful when looking at different cell organelles and cellular structures.
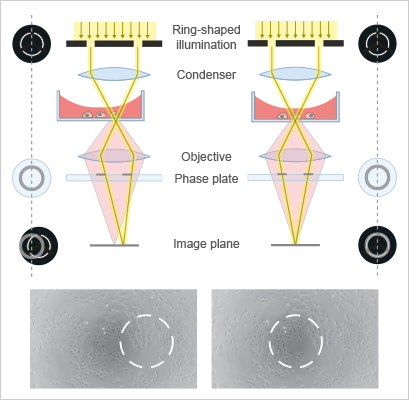
Phase Contrast Microscopy Principle And Applications Ibidi
By generating constructive interference between scattered and background light rays in regions of the field of view that contain the specimen and by reducing.

. The amplitude of the light. The darkfield microscope is a conventional. Analytical Technologies in Biotechnology Dr.
Differences Between Bright and Dark Field Microscopes Bright vs Dark Field Microscopes If you are a man of science you probably love microscopes. The dark field microscope produces a light cone which reaches the objective only when it is scattered by the sample. This microscope also uses an opaque ring or annular stop but this one has a transparent ring that only releases light in a hollow cone.
A counterstain is then applied to give a different color to the now colorless Gram-negative bacteria. Describe at least 4 different approaches to Transmission Electron Microscopy TEM sample preparation. Define and distinguish between magnification and resolution.
Think of the light source as producing a solid tube of light that travels up to and through the condenser. Phase-contrast- transforms subtle changes in light waves passing through the specimen into differences in light. Phase-contrast microscopymakes use of a specific optical system that converts differences.
Microscopes are useful tools that help us see the unseen. This leads to the foreground blue vector and background red vector having nearly the same intensity resulting in low image contrast. An amplitude specimen decreases the intensity ie.
Definition of Dark Field Microscope. In a phase-contrast microscope image contrast is increased in two ways. This reinforces the image contrast.
View Dark-field and Phase Contrast Microscopypdf from BIOTECHNOL 221 at National Institute of Technology Warangal. Compare and contrast the key characteristics of a synthesis versus decomposition versus a displaceme. Sub-stage annular diaphragm phase condenser An annular aperture in the diaphragm is placed in the focal plane of the sub-stage which controls the illumination of the object.
Used for live and unstained specimens. In phase in an organism into differences in intensity of light thereby producing light and dark contrast in the image Fig. Dark field and phase contrast microscopes allow to observe transparent samples.
Explain the difference between phase contrast and amplitude contrast in the Transmission Electron Microscopy TEM. Dark-field- brightly illuminated specimens surrounded by dark field. It is suitable for observing the natural colors of a.
Bright field lighting is the more commonly applied lighting geometry which involves mounting and orienting lights between 90 and 45 degrees from the imaging surface off horizontal. The phase contrast microscope modifies the light trajectory so that part of the beam is modified by the sample and. For this purpose the red dye safranin is used.
Phase specimens cause a phase shift of the light. Prior to phase contrast microscopy specimens would need to be stained or otherwise manipulated in order be seen under a standard brightfield microscope. The most obvious difference between DIC and phase contrast microscopy is the pseudo three-dimensional shadow-cast images formed by differential interference contrast optical systems.
When light passes through transparent specimens a small phase shift occurs which cant be detected by our eyes. In bright-field microscopy illumination light is transmitted through the sample and the contrast is generated by the absorption of light in dense areas of the specimen. This is located below the condenser of the microscope.
Specimen images are rendered in a manner reminiscent of the shadowing techniques utilized for many years in electron microscopy which yield information on. The optical system includes a special condenser and objec-tive lens which can be fitted to an ordinary light microscope to convert it. The limitations of bright-field microscopy include low contrast for weakly absorbing samples and low resolution due to the blurry appearance of out-of-focus material.
Definition of Bright Field Microscope. 1Synthesis reaction- It is the are chemical reactions where two elements are combine to make a pro. Conversely dark field lighting involves orienting lights between 0 and 45 degrees off horizontal which is particularly effective when imaging highly reflective surfaces or generating.
Phase Contrast Microscope is an optical microscope that converts small phase shifts in light into differences in light intensity developing more contrast in images that can be easily detected by human eyes. A phase contrast microscope differs from bright field microscope in having i. The invention of microscopes.
Different Types of Microscopy. This dye enter Gram-positive cells as well but because they are already purple it makes little difference to their color. The type of illumination that you are most familiar is called Bright Field.
This phase shift can not be detected with the unaided eye and requires a phase contrast microscope. Explain the difference between bright field and dark field imaging in the Transmission Electron Microscopy TEM. There are three different ways that we can view specimens with these microscopes.
The Working of Phase contrast Microscopy Partially coherent illumination produced by the tungsten-halogen lamp is directed through a collector lens and focused on a specialized annulus labeled condenser. Darkfield microscopy shows the specimens bright on. Describe the basic differences between Light Microscopy bright field dark field phase- contrast and fluorescent and Electron Microscopy Transmission and Scannin 3.
Bright field microscopy is the conventional technique. Air is completely transparent I hope you agree. Specimen is darker than surrounding field and is used for live and preserved stained specimens.
In a phase-contrast microscope these phase shifts are converted into changes in amplitude which can be observed as differences in image contrast. The phase-contrast microscope is also a modified bright-field microscope although the modifications are getting more complex as well as more expensive. Brightfield -most widely used.
Bright Field Dark Field and Phase-Contrast. The Bright Field Microscope is a conventional Microscope in this microscope the specimen appears as dark against a bright background. Describe 4 extracellular structures unique to prokaryotes explain the function of each.
With just our naked eyes we wont be able to see the tiniest speck of an organism or the tiniest structure of a nonliving object. What are the differences between brightfield darkfield and phase contrast.

Figure 5 This Diagram Of A Phase Contrast Microscope Illustrates Phase Differences Between Light Passing Microbiology Microscopy Scanning Electron Microscope
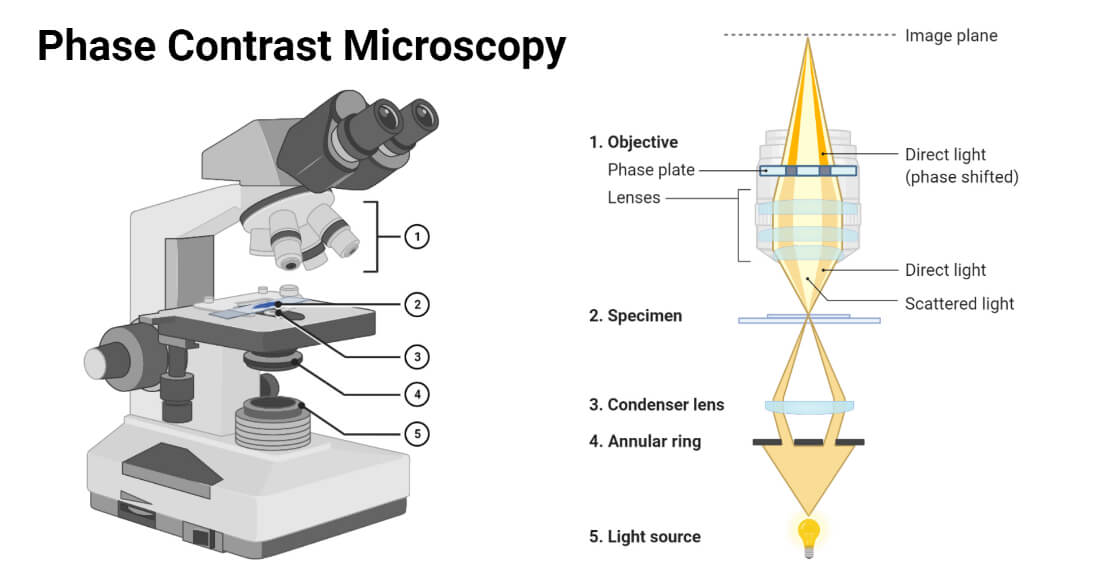
Phase Contrast Microscopy Definition Principle Parts Uses
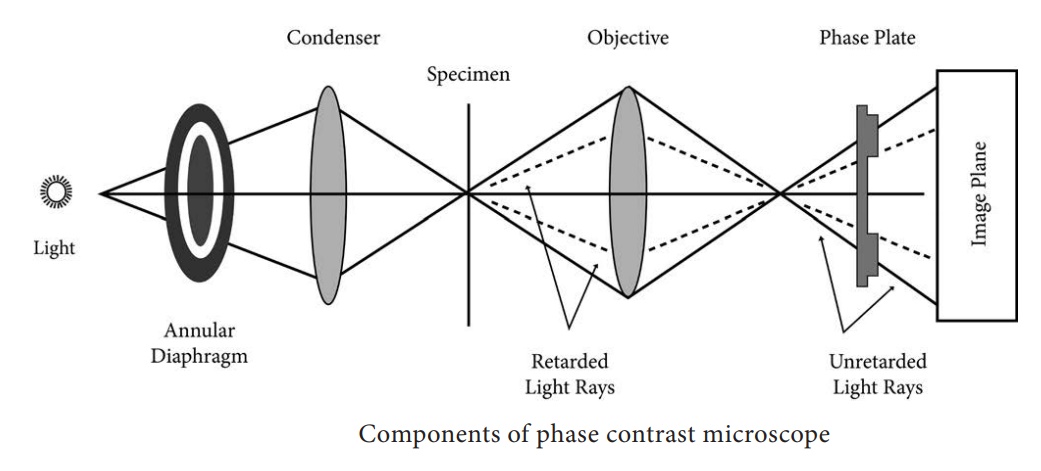
Phase Contrast Microscope Principle Working Mechanism Applications Optical Components
Comments
Post a Comment